Discover Gua Sha Benefits: Health, Science, and Origins Explained

Overview
This article delves into the numerous benefits of Gua Sha, a traditional Chinese medicine technique renowned for its capacity to enhance circulation, reduce inflammation, alleviate chronic pain, and improve skin health. By elucidating the physiological mechanisms underpinning Gua Sha—such as increased microcirculation and immune system stimulation—it substantiates these claims. Furthermore, the article highlights the historical significance of Gua Sha and its contemporary integration into wellness practices, encouraging readers to explore its potential in their own health regimens.
Introduction
Gua Sha, an ancient practice rooted in traditional Chinese medicine, has emerged as a prominent wellness trend, captivating individuals in pursuit of holistic health solutions. This technique, which involves scraping the skin's surface with a smooth tool, offers a myriad of benefits, including improved circulation and enhanced skin texture.
As its popularity continues to rise, however, questions regarding the authenticity of its cultural origins and the potential for misapplication in modern contexts have surfaced. What are the genuine benefits of Gua Sha, and how can this time-honored practice be seamlessly integrated into contemporary health regimens without compromising its essence?
Define Gua Sha: Origins and Historical Context
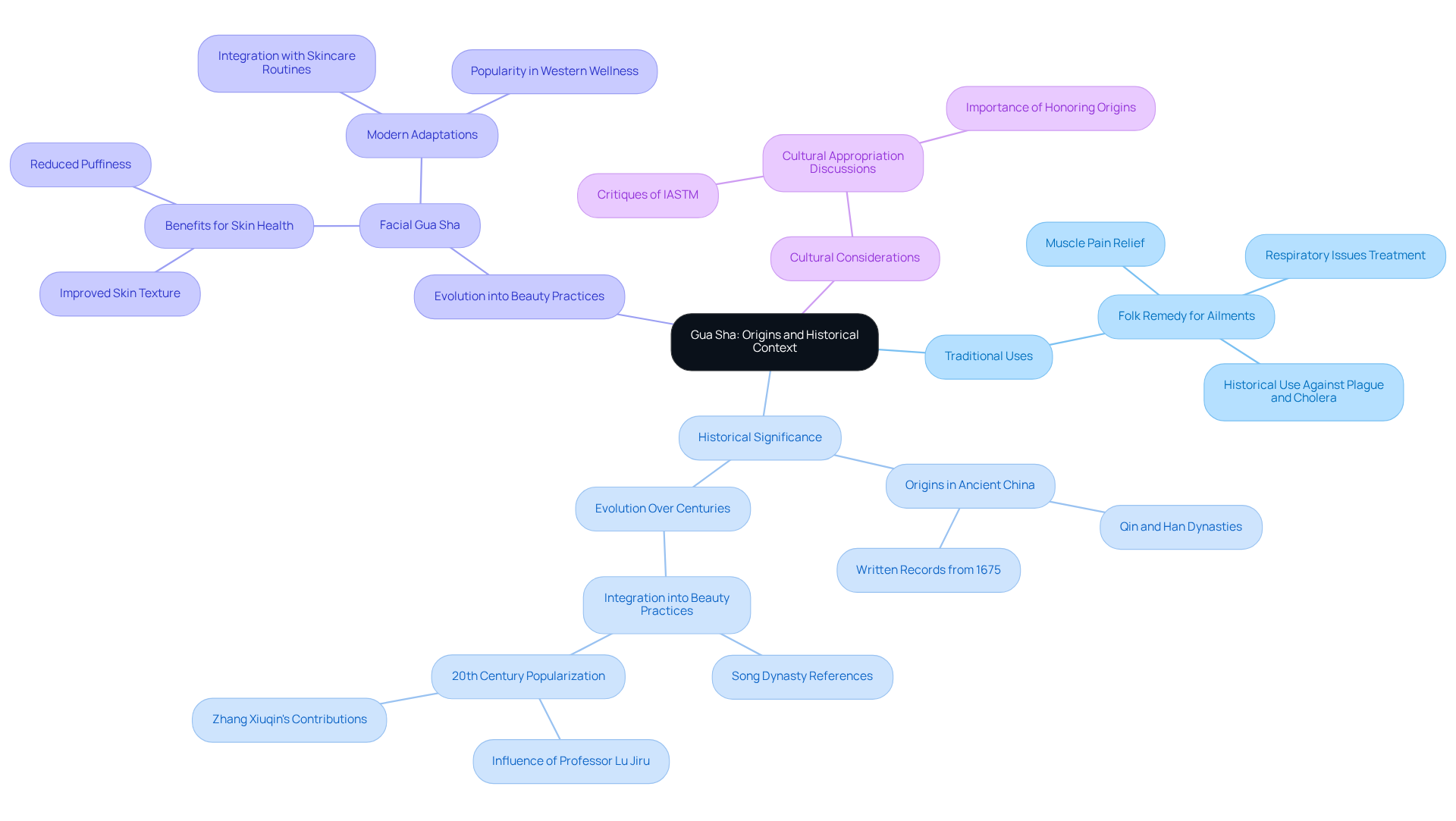
Gua Sha is a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves scraping the skin's surface with a smooth-edged tool, often crafted from jade or other materials. This practice has its origins in ancient China, dating back over 5,000 years, where it was utilized as a folk remedy for a variety of ailments, including muscle pain and respiratory issues. The term 'Gua Sha' translates to 'scrape away fever,' highlighting its historical role in alleviating symptoms of illness. Initially, Gua Sha was primarily focused on treating serious diseases, as evidenced by historical texts documenting its use against ailments such as the plague and cholera. The earliest written records of Gua Sha can be traced back to the Qin and Han Dynasties, offering a deeper historical context for its practice.
Over the centuries, Gua Sha has experienced significant development, evolving from a therapeutic remedy to a recognized practice that highlights the gua sha benefits for enhancing overall well-being, particularly within East Asian cultures. Notably, references to jade rubbing on the face for scar treatment emerge from the Song Dynasty (960-1127 AD), marking the early integration of Gua Sha into beauty practices. In the 20th century, influential figures like Professor Lu Jiru and Zhang Xiuqin were instrumental in popularizing Gua Sha for facial beauty, effectively merging traditional techniques with modern skincare routines.
Today, Gua Sha is increasingly embraced in Western wellness and beauty circles due to its gua sha benefits, which include . However, its roots remain deeply entrenched in holistic wellness practices, emphasizing the interconnectedness of internal well-being and external appearance, as outlined in ancient texts like the Huangdi Neijing. This historical context emphasizes the necessity of recognizing Gua Sha not merely as a beauty treatment but as a practice imbued with profound cultural and therapeutic significance. Furthermore, contemporary discussions surrounding Gua Sha include critiques of Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM) as a form of cultural appropriation, underscoring the importance of honoring its origins while integrating it into modern practices.
Explore the Health Benefits of Gua Sha
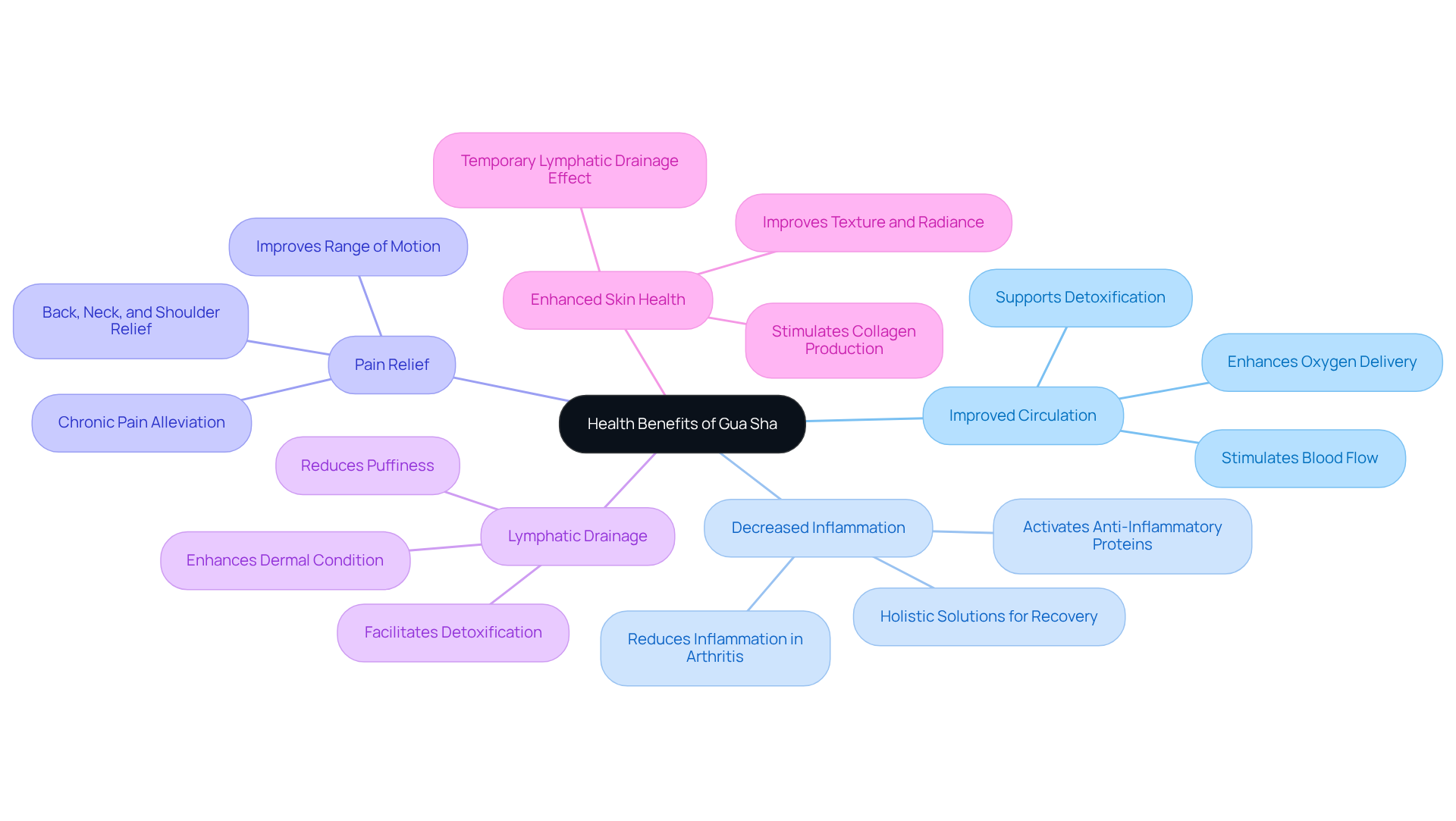
Gua Sha serves as a pivotal tool in both traditional and modern wellness practices, providing numerous gua sha benefits that can enhance overall well-being. Key advantages include:
- Improved Circulation: The scraping motion of Gua Sha stimulates blood flow, significantly enhancing the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to tissues. This improved circulation not only enhances appearance and tone but also contributes to overall vitality. At Tsavo Wellness, we recognize that enhancing circulation is essential for well-being, complementing our advanced lymphatic massage therapies designed to support your body's natural detoxification processes.
- One of the gua sha benefits is its ability to effectively decrease inflammation throughout the body, making it particularly beneficial for conditions such as arthritis and muscle soreness. Research suggests that this technique may activate anti-inflammatory immune proteins, contributing to systemic relief. This aligns with our commitment at Tsavo Wellness to provide holistic solutions that address inflammation and promote recovery.
- Many individuals report substantial relief from chronic pain, particularly in the back, neck, and shoulders, highlighting the gua sha benefits experienced after treatments. A study revealed that adults with chronic neck pain experienced significant improvements in pain severity after just one session. Dr. Houman Danesh emphasizes that Gua Sha promotes blood flow to the area being treated, which can alleviate pain and stiffness. Our offerings, including the Slimyonik Air Bodystyler, further enhance recovery and pain management through state-of-the-art lymphatic massage compression therapy.
- Gua sha benefits include promoting lymphatic drainage, facilitating detoxification, and reducing puffiness, especially in facial applications. The temporary lymphatic drainage effect can enhance dermal condition and appearance, although it requires proper technique to avoid negative effects. At Tsavo Wellness, we stress the importance of lymphatic health, integrating Gua Sha with our advanced therapies to maximize detoxification benefits.
- Regular facial Gua Sha use can provide gua sha benefits such as improved texture, diminished fine lines, and a more radiant appearance, leading to enhanced complexion health. Dermatologists note that while the effects may be temporary, consistent application can stimulate collagen production and enhance overall dermal function. Our red light therapy treatments at Tsavo Wellness amplify these benefits by stimulating cellular activity and encouraging rejuvenation.
The gua sha benefits underscore Gua Sha's holistic approach to health, effectively addressing both physical ailments and aesthetic concerns, making it a sought-after practice in wellness routines. However, it is crucial to approach Gua Sha with care, as improper technique may lead to bruising or tearing. We recommend consulting with at Tsavo Wellness to maximize benefits and minimize risks.
Understand the Science: How Gua Sha Works
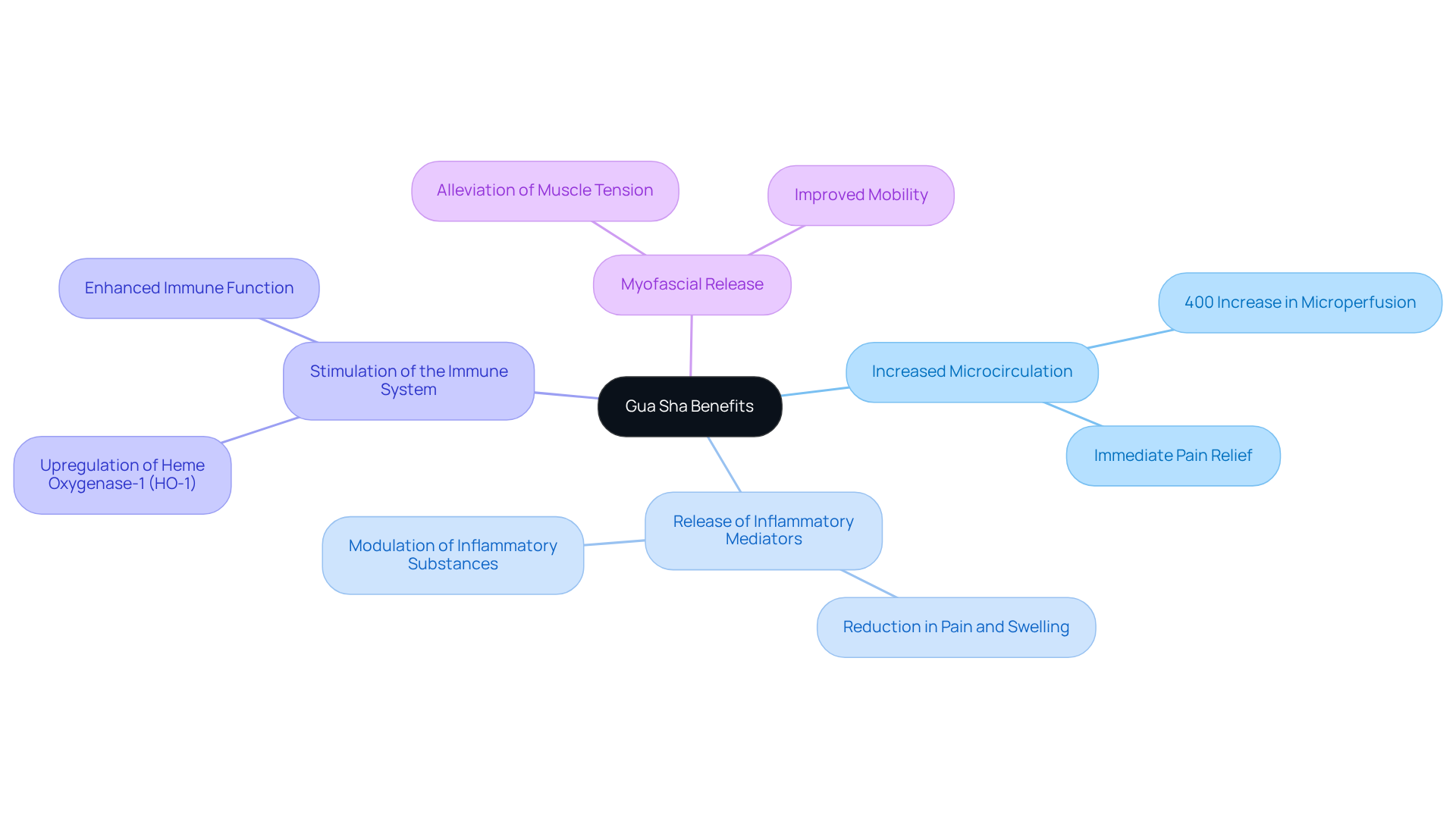
The effectiveness of Gua Sha benefits is based on several physiological mechanisms that yield significant therapeutic effects. When the skin is scraped with a smooth-edged tool, it induces microtrauma, prompting a robust healing response from the body. This response includes:
- Increased Microcirculation: Research demonstrates that Gua Sha markedly enhances local blood flow, with studies revealing an impressive 400% increase in microperfusion immediately following treatment. This surge in circulation not only alleviates pain but also promotes healing.
- Release of Inflammatory Mediators: The technique appears to modulate the release of inflammatory substances, effectively reducing pain and swelling. This illustrates the Gua Sha benefits, making it particularly advantageous for conditions characterized by inflammation.
- Stimulation of the Immune System: Gua Sha has been shown to bolster immune function, potentially enhancing the body's capacity to combat illness. This immune stimulation is associated with the upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), an enzyme recognized for its anti-inflammatory properties.
- Myofascial Release: The scraping action of Gua Sha effectively alleviates tension in the fascia, the connective tissue enveloping muscles. This release can enhance mobility and diminish discomfort, particularly in areas affected by chronic pain.
In addition to Gua Sha, Tsavo Wellness offers Red Light Therapy (RLT), a non-invasive, non-thermal treatment that complements the Gua Sha benefits. RLT addresses the entire system in just 20 minutes, stimulating cellular repair and regeneration, reducing inflammation, and enhancing recovery. This makes it an excellent choice for athletes aiming to train harder without adverse effects. Many clients report significant results after just one session, underscoring the effectiveness of combining these therapies. These scientific insights not only validate the traditional claims surrounding Gua Sha but also highlight the Gua Sha benefits in contemporary wellness practices. As a complementary therapy, Gua Sha benefits, along with RLT, provide a natural approach to addressing various health issues, reinforcing its status as a valuable tool in holistic health.
Conclusion
Gua Sha represents a powerful convergence of ancient tradition and contemporary wellness, embodying a holistic approach that goes beyond superficial beauty treatments. This practice, deeply embedded in Chinese medicine, offers a multitude of health benefits that significantly enhance both physical and aesthetic well-being. By recognizing its historical significance and therapeutic potential, individuals can appreciate Gua Sha not merely as a skincare ritual but as an essential aspect of overall health enhancement.
The article has delved into key insights regarding Gua Sha's benefits, notably its capacity to:
- Improve circulation
- Reduce inflammation
- Alleviate chronic pain
- Promote lymphatic drainage
Scientific evidence substantiates these claims, demonstrating how Gua Sha stimulates microcirculation and immune responses, thereby affirming its efficacy in modern wellness practices. The synergy of Gua Sha with additional therapies, such as Red Light Therapy, further amplifies its healing properties, rendering it a valuable asset for those pursuing comprehensive health solutions.
Understanding the importance of Gua Sha extends beyond its immediate advantages; it encourages a broader contemplation of the necessity to honor cultural origins while embracing contemporary adaptations. As the interest in holistic health continues to escalate, integrating Gua Sha into daily routines can cultivate a deeper connection to well-being. Embrace this ancient practice not solely for its aesthetic allure but as a transformative experience that nurtures both body and spirit, paving the way for a healthier, more vibrant life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Gua Sha?
Gua Sha is a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves scraping the skin's surface with a smooth-edged tool, often made from jade or other materials, to alleviate various ailments.
What are the historical origins of Gua Sha?
Gua Sha originated in ancient China over 5,000 years ago and was used as a folk remedy for ailments such as muscle pain and respiratory issues. The term 'Gua Sha' translates to 'scrape away fever,' reflecting its historical role in treating symptoms of illness.
How was Gua Sha used in ancient times?
Initially, Gua Sha focused on treating serious diseases, with historical texts documenting its use against ailments like the plague and cholera. The earliest written records date back to the Qin and Han Dynasties.
How has Gua Sha evolved over the centuries?
Gua Sha has evolved from a therapeutic remedy to a recognized practice for enhancing overall well-being, particularly in East Asian cultures. It began to integrate into beauty practices during the Song Dynasty, with references to jade rubbing for scar treatment.
Who contributed to the popularity of Gua Sha in the 20th century?
Influential figures such as Professor Lu Jiru and Zhang Xiuqin played significant roles in popularizing Gua Sha for facial beauty, merging traditional techniques with modern skincare routines.
What are the contemporary benefits of Gua Sha?
Today, Gua Sha is embraced in Western wellness and beauty circles for its benefits, which include improved skin texture and reduced puffiness, while still emphasizing holistic wellness.
Why is it important to recognize the cultural significance of Gua Sha?
Gua Sha is not just a beauty treatment; it holds profound cultural and therapeutic significance. Contemporary discussions also critique practices like Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM) as cultural appropriation, highlighting the importance of honoring its origins.


